B.Sc. (Nursing) Degree Examination
Fourth semester
(Revised/Modified Regulations)
Paper I - Principles and Practice of Adult Nursing/Medical Surgical Nursing
Time : Half an hour Maximum : 20 marks
Paper I - PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE OF ADULT NURSING /MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING
SECTION -C (15 x 1 = 20 marks)
(Multiple Choice Questions)
Select the most appropriate response.
1. Typhoid fever is transmitted by
a) Contaminated food and fluid
b) Droplet nuclei
c) Infected syringes and needles
d) Sexual intercourse
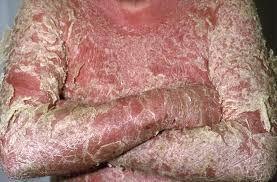
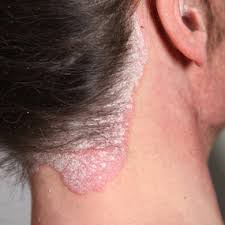
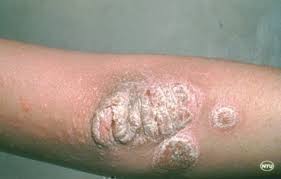
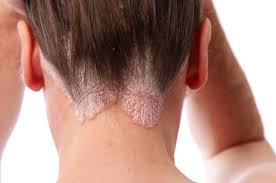
2. Red raised patches of skin covered with silvery scales is seen in
a) Scabies
b) Pemphigus vulgaris
c) Psoariasis
d) Contact dermatitis
3. The normal serum potassium level is
a) 2- 2.5 mEq / liters
b) 2.1 - 2.3 mEq / litre
c) 6 - 6.5 mEq / litre
d) 3.5 - 5.5 mEq / litre
4. The primary goal in withholding food before surgery is to prevent
a) Abdominal distension
b) Aspiration
c) Infection
d) Obstruction
5. When vomiting occurs in the immediate post-operative period, most important nursing intervention is to
a) Measure the amount and record
b) Offer tepid water or juice
c) Support the wound
d) Turn the patient's head to one side to prevent aspiration into the lungs
6. An early sign of cancer of the larynx is
a) Burning of throat when hot liquids are ingested
b) Enlarged cervical nodes
c) Hoarseness of voice
d) Dysphagia
7. Nursing intervention for a patient who is scheduled for bronchoscopy includes
a) An informed consent to be obtained
b) Food and fluids are withheld for 6 hours before the test
c) preanesthetic medication is given as prescribed
d) All of the above
8. The drug of choice for bacterial pneumonia is
a) Erythromycin
b) Penicillin G
c) Clindamycin
d) Streptomycin
9. The most specific enzyme analysis in the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction is
a) Serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT)
b) Creatine kinase (CK)
c) Serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase (SGPT)
d) Aspartate aminoatransferase (AST)
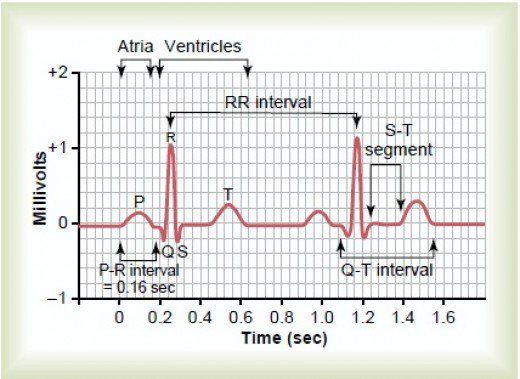
10. QRS complex in an ECG represents
a) Atrial muscle depolarization
b) Atrial muscle re-polarization
c) Ventricular muscle depolarization
d) Ventricular muscle repolarization
11. A common side effect of nitroglycerine is
a) Musculo - skeletal weakness
b) Hypertension
c) Headache
d) Bradycardia
12. Rheumatic endocarditis is an inflammatory reaction to
a) Pseudomonas aerugenosa
b) Staphylococcus aureus
c) Group A streptococcus
d) Serratio marcescens.
13. Post operative nursing management for vein ligation and stripping include all of the following except :
a) Dangling the legs over over the side of the bed for 10 minutes every 4 hours for the first 24 hours
b) Elevating the foot of the bed to promote venous blood return
c) Maintaining elastic compression of the leg for 1 week
d) Ambulating the patient 24-48 hours after surgery
14. For a patient diagnosed as having iron deficiency anemia, the nurse should recommend an increased intake of
a) Fresh citrus fruits
b) Milk and cheese
c) Organ meat
d) Whole grain bread.
15. The major cause of death in patients with leukemia is believed to be
a) Fever
b) Melena and haematuria
c) Infection
d) Dehydration